Spark企业法人建模案例
数据格式如下:
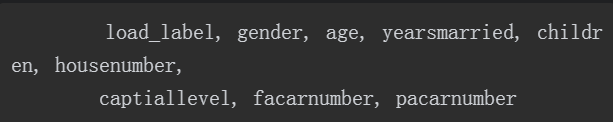
字段含义参考上一节。
样例如下:
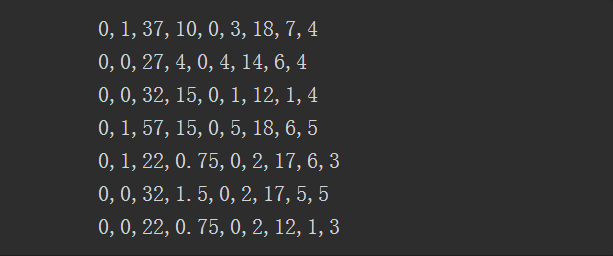
package com.koala.ch12
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.VectorAssembler
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.LogisticRegression
object CreditModel {
// 创建评分模型属性class,对字段进行命名
// 0,1,37,10,0,3,18,7,4
case class Credit(load_label:Double,gender:Double,age:Double,yearsmarried:Double,children:Double,housenumber:Double,captiallevel:Double,facarnumber:Double,pacarnumber:Double)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.WARN)
if (args.length < 3){
System.err.println("Usage:CreditModel <creaditInPath> <outPut> <model>")
System.exit(1)
}
//2rd_data/ch12/creditdata.txt output/ch12/model local[2]
val Array(creaditInPath,output,mode) = args
// 创建Spark实例
val spark = SparkSession.builder
.master(mode)
.appName("CreditModel Example")
.getOrCreate()
// 加载文本,并创建RDD数据源,将变量的名称赋予各个字段
// Create an RDD of Credit objects from a text file, convert it to a Dataframe
import spark.implicits._
val creditDF = spark.sparkContext.textFile(creaditInPath).map(_.split(","))
.map(attributes => Credit(attributes(0).trim.toDouble,attributes(1).trim.toDouble,attributes(2).trim.toDouble,attributes(3).trim.toDouble,attributes(4).trim.toDouble,attributes(5).trim.toDouble,attributes(6).trim.toDouble,attributes(7).trim.toDouble,attributes(8).trim.toDouble))
.toDF()
// Register the DataFrame as a temporary view
// 创建临时视图
creditDF.createOrReplaceTempView("creditdf")
// 将查询结果放到sqlDF中,完成dataframe转化
val sqlDF = spark.sql("select * from creditdf")
sqlDF.show()
// 自变量的列名
val colArray2 = Array("gender","age","yearsmarried","children","housenumber","captiallevel","facarnumber","pacarnumber")
// 设置DataFrame自变量集,并将这些变量统称为"features"
val vecDF: DataFrame = new VectorAssembler().setInputCols(colArray2).setOutputCol("features").transform(sqlDF)
// 按7:3划分成训练集和测试集,训练集为trainingDF,测试集为testDF
val Array(trainingDF,testDF) = vecDF.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3), seed=132) //seed随机算法从该数字开始生成随机数字
// 建立逻辑回归模型,设置目标变量(标签)和自变量集,在训练集上训练
val lrModel = new LogisticRegression().setLabelCol("load_label").setFeaturesCol("features").fit(trainingDF)
// 输出逻辑回归的系数和截距
println(s"Coefficients: ${lrModel.coefficients} Intercept: ${lrModel.intercept}")
// 惩罚项,如果是0,是L2惩罚,如果是0-1之间是混合,如果是1,则是L1惩罚,默认是L2
lrModel.getElasticNetParam
// 正则化的参数,一般大于等于0,默认是0
lrModel.getRegParam
// 拟合之前是否需要标准化,默认是true
lrModel.getStandardization
// 二分类中设置阈值,范围为[0,1],如果类标签的1的概率大于该阈值,则会判定为1,默认是0.5
lrModel.getThreshold
// 设置迭代的收敛容限,默认值为1e-6
lrModel.getTol
// 使用测试集进行预测,包括原始的字段,在加上综合的自变量集字段features,预测的原始值,转化的概率值,预测的类别
lrModel.transform(testDF).show
//具体的查看features,预测的原始值,转化的概率值,预测的类别
lrModel.transform(testDF).select("features","rawPrediction","probability","prediction").show(30,false)
//查看模型训练过程中损失的迭代情况
val trainingSummary = lrModel.summary
val objectiveHistory = trainingSummary.objectiveHistory
objectiveHistory.foreach(loss => println(loss))
//保存模型
lrModel.save(output)
//
spark.close()
}
}